作者:Tao Wang , Tingting Lin , Zhiquan Liu , Xiao Xie , Shihong Yao
出版刊物:Information Fusion
出版时间:2025年
内容摘要:
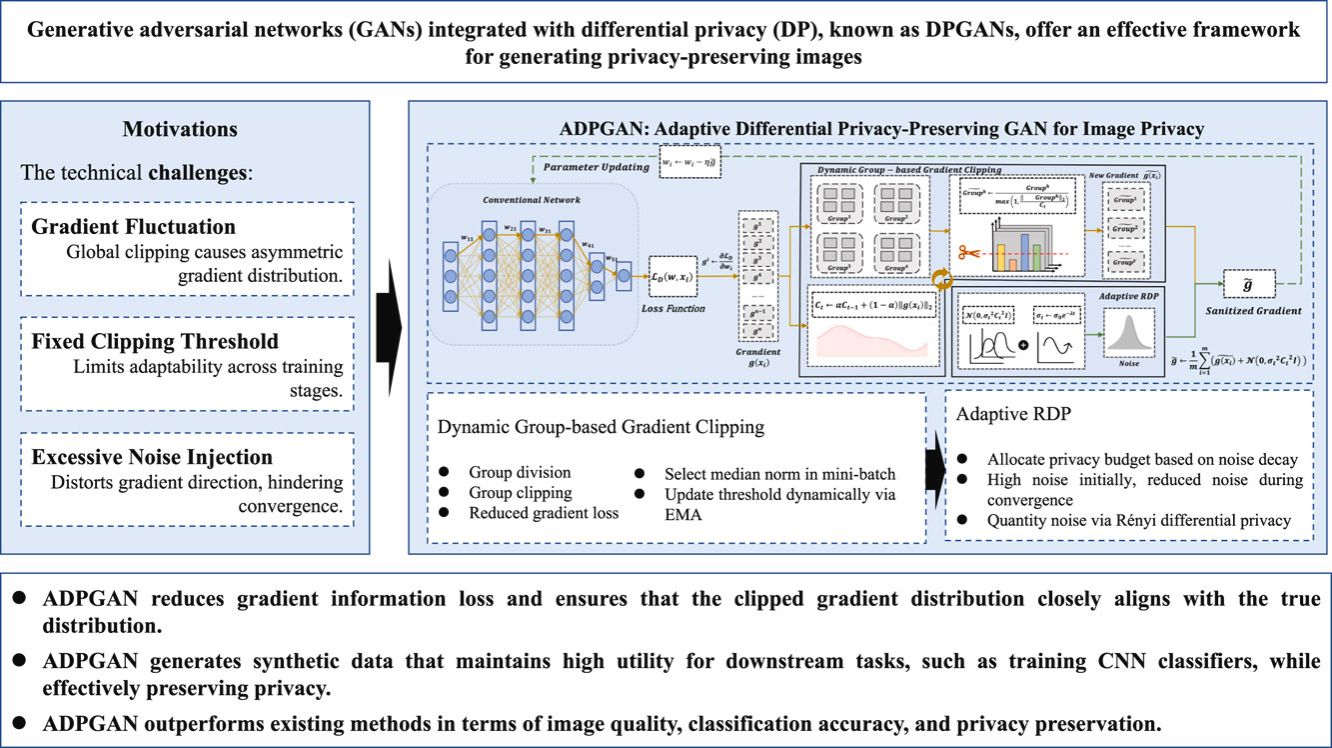
With the development of image acquisition and social network technologies, the volume of image data has surged, highlighting the contradiction between data publication and privacy security. In this context, generative adversarial networks (GANs) provide a breakthrough solution to strike a balance between image data development and privacy protection. Many scholars have enhanced privacy protection by adding a certain scale of noise during GAN training, enabling the generation of highly useful synthetic data that satisfies privacy requirements. However, the introduction of noise in GANs leads to model instability and compromises usability. We focus on the application of GANs in the field of image privacy protection and propose an adaptive differential privacy-preserving GAN framework, called ADPGAN. First, we introduce a dynamic group-based gradient clipping method, which divides gradients into multiple subgroups for truncation and employs exponential moving averages to continuously optimize the clipping threshold. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that this dynamic adjustment mechanism significantly mitigates the information loss inherent in traditional fixed-threshold clipping methods. Second, we design an adaptive Rényi differential privacy (RDP) mechanism that dynamically optimizes noise levels based on the model’s training state. By leveraging Rényi differential privacy to precisely quantify noise, this mechanism further ensures the stability and performance of ADPGAN, effectively improving convergence speed and the quality of generated images. Finally, we conduct experimental validation on three benchmark image datasets: MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and Flowers-Recognition. The results show that ADPGAN achieves significant improvements compared to state-of-the-art methods (with the downstream classification accuracy increasing by up to 7.44%) while providing image privacy protection. Furthermore, a rigorous privacy analysis confirms that the proposed method fully complies with differential privacy requirements, offering a solid theoretical and practical foundation for the application of GANs in privacy-preserving scenarios.
随着图像采集与社交网络技术的飞速发展,图像数据量激增,数据开放与隐私安全之间的矛盾日益凸显。在此背景下,生成对抗网络为平衡图像数据开发与隐私保护提供了突破性解决方案。众多学者通过在GAN训练过程中添加特定规模噪声的方式强化隐私保护,从而生成满足隐私要求的高可用合成数据。然而,噪声引入会导致模型失稳并影响数据可用性。
本研究聚焦GAN在图像隐私保护领域的应用,提出了一种自适应差分隐私保护GAN框架——ADPGAN。首先,我们提出动态分组梯度裁剪方法,将梯度划分为多个子组进行截断处理,并采用指数移动平均持续优化裁剪阈值。理论分析表明,这种动态调整机制能显著缓解传统固定阈值裁剪方法固有的信息损失问题。其次,我们设计了自适应Rényi差分隐私机制,可根据模型训练状态动态优化噪声水平。该机制利用Rényi差分隐私实现噪声精准量化,进一步确保ADPGAN的稳定性和性能表现,有效提升收敛速度与生成图像质量。最后,我们在MNIST、Fashion-MNIST和Flowers-Recognition三个基准图像数据集上开展实验验证。结果表明,ADPGAN在实现图像隐私保护的同时,相比现有最优方法取得显著提升(下游分类任务准确率最高提升7.44%)。此外,严格的隐私分析证实,所提方法完全满足差分隐私要求,为GAN在隐私保护场景的应用提供了坚实的理论与实践基础。